

Natural Parameters EStimation (NPES) vocoder
This technology of digital representation (coding)
of speech is based on "natural" model of speech production.
Under this model the speech signal is represented with set of parameters
which values vary in the time and define the state of human vocal
tract elements during speech sound speaking. Because of vocal tract
state under articulation vary comparatively slow in the time
it is possible to consider model parameters as locally constant on
speech signal zones (segments) at length 15-20 milliseconds.
Moreover the set of different speech sounds is finite and so it is possible
to approximate all parameter's area with finite numbers of values
by juxtapose each speech signal segment with some number (code).
This method of digital speech representation allow to decrease in
dozens of times the space required for its transfer and storing.
Besides the parameter's physical conditionality and completeness allow
to use this technology in tasks of speaker identification, speech
recognition and synthesis.
Vocoder structure
Functionally NPES vocoder consists of four parts each of that perform digital representation (format) transformation of speech signal. Analyser procedure transform speech signal segment from sample sequence representation (PCM format) into model parameter's values and synthesis procedure perform reverse conversion. Coding procedure lets juxtapose each parameter value assembly with 32-bit number (NPES format) and decoding procedure perform reverse action.
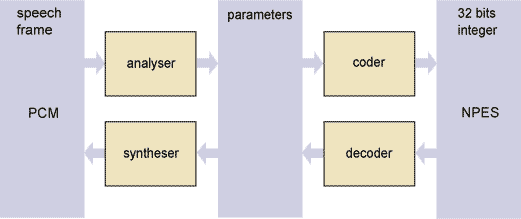
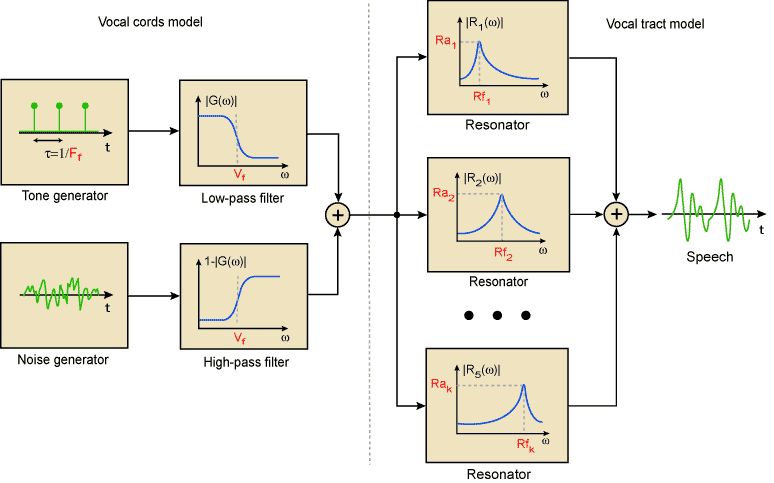
Speech model
Model of speech production which lie in the base of NPES vocoder consist of two independent parts. 1st one describes vocal chord operations and 2nd one - articulation organ processing. Vocal chord parameters are general pitch and vocalization frequencies ( Ff,Vf ). General pitch frequency determine vocal chord vibration in voiced sound pronouncing ( [a], [o] ). Vocalization frequency determine stochastic component quantity in partially voiced and unvoiced sound pronouncing ( [s], [h], [z] ). Articulation organ model parameters are resonator frequencies and amplitudes ( Rak, Rfk ) wich selected so that model gain-frequency characteristic should compare most precisely with formant structure of the speech signal.
Model parameter values can be easily found over speech signal momentary spectrum. That makes its visualization more easy and lets to learn its behaviours with well known programs for sound processing.
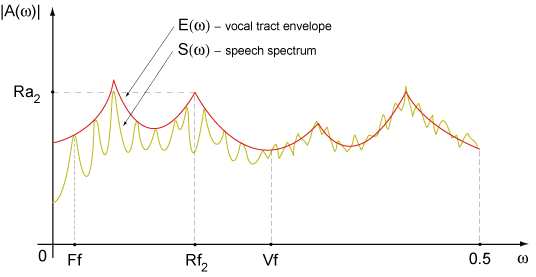
Speech compression
The main field of application for NPES vocoder is telecommunications. The required channel carrying capacity for speech signal coding transfer in real time is its primary characteristic. Usually this value is measured in BPS (Bits Per Second). NPES vocoder lets vary the analyse/synthesis segment size and number of segments per second (SPS) in processing, thereby varing the transfer speed required (BPS = SPS * 32). The following table contain speech coding quality results depending on transfer speed.
|
Source speech
|
Bitrate (BPS)
|
Speech quality (MOS)
|
| Male voice | 1280 | 3.17 |
| 1600 | 3.25 | |
| 2000 | 3.26 | |
| Female voice | 1280 | 2.96 |
| 1600 | 3.06 | |
| 2000 | 3.18 |
- The speech quality was measured according to ITU-T P.861 recommendation.
- Processing delay for all transfer rates - 25 ms.
- All sample signals are digitized at 8 KHz sample rate and 16 bits per sample.
Speech transformation
Due to the fact that mathematical model parameters NPES vocoder based on correspond to physical characteristics of vocal apparatus elements, its values measured for one speaker can be easily changed to conform to the voice of another speaker or different pronouncing manner. This important feature can have number of applications. For example the voice general pitch can be corrected according to music notes. It lets to use NPES vocoder for karaoke applications. The following table contain examples of transformation for general pitch and vocal tract length.
|
Source speech
|
Transformed speech
|
| Male voice | voice pitch: + 1 octave, vocal tract size: 80 % |
| Female voice | voice pitch: - 2 octave, vocal tract size: 120 % |
Hardware and software requirements
The following table contain NPES vocoder computational requirements for Pentium III 800 MHz CPU and Windows XP operating system.
Module |
CPU utilization (%) |
RAM (Kb) |
ROM (Kb) |
analysis |
12 |
270 |
30 |
synthesis |
5 |
25 |
15 |
analysis+synthesis |
17 |
280 |
35 |
analysis+coder |
15 |
271 |
155 |
synthesis+decoder |
5 |
26 |
145 |
analysis+synthesis+coder+decoder |
20 |
282 |
165 |
- CPU utilization means the required part of computational resources of the system to invoke process in real time. It depends on source data sample rate and speech characteristics. The table contain averaged values calculated with command line utilities from NPES SDK.
- RAM value is memory size required for variables and stack.
- ROM value is memory size required for constants and program code.
technologies | programs | papers | links | about | NPES vocoder | NPES SDK | ADSS filter | ADSS SDK | Fork | VoiceVary | SoundClear | P861 | P56 |
© Phrase Research Group, 2002 © Phrase-Art, 2002